Starting with the definition of the Hessian Matrix, this posting will focus on the geometric meaning of the Hessian matrix. Also, we will discuss the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the Hessian and introduce the application of it.
This post was written with reference to the following materials.
Hessian Matrix
Definition
In mathematics, the Hessian matrix or Hessian is a square matrix of second-order partial derivatives of a scalar-valued function, or scalar field. It describes the local curvature of a function of many variables. [1]
Suppose $f : ℝ^n → ℝ$ is a function taking as input a vector $x ∈ ℝ^n$ and outputting a scalar $f(x) ∈ ℝ$. If all second partial derivatives of $f$ exist and are continuous over the domain of the function, then the Hessian matrix $H$ of $f$ is a square n×n matrix, usually defined and arranged as follows; [1]
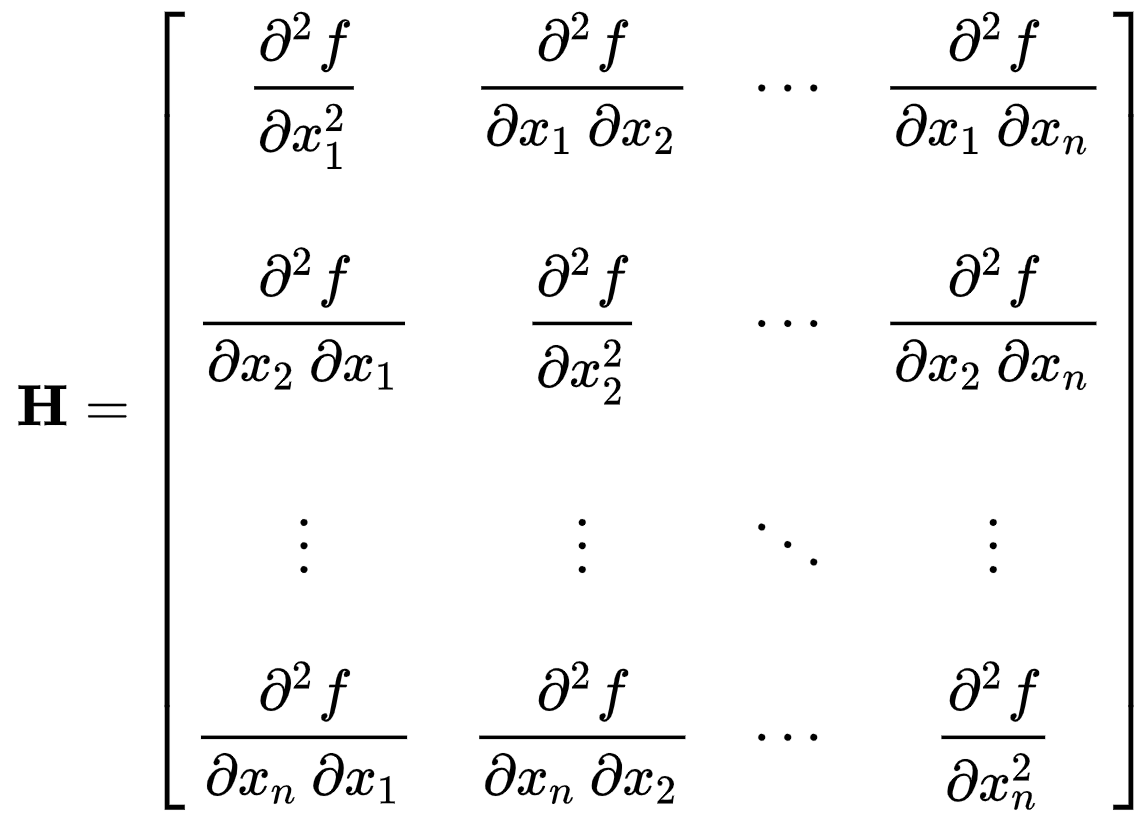
Geometric Meaning
First of all, it is well known that all matrices can be considered as linear transformations. Likewise, we can think of a Hessian matrix as a linear transformation. Geometrically, the main feature of the linear transformation performed by the Hessian matrix is to make a given function more convex or concave.
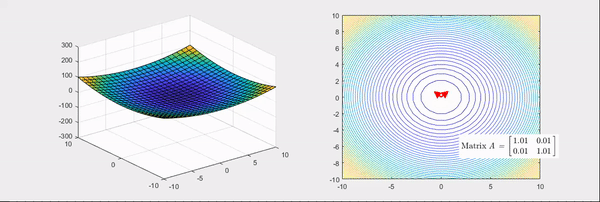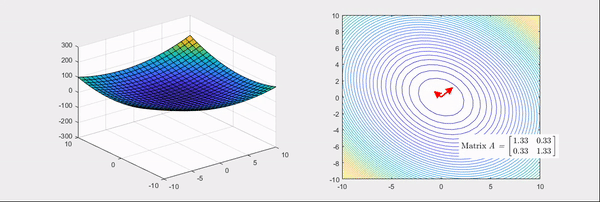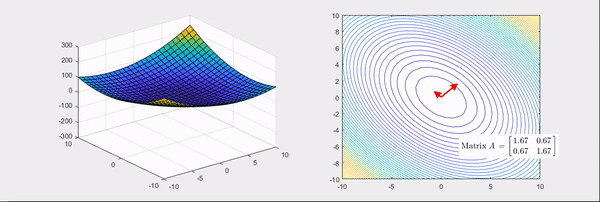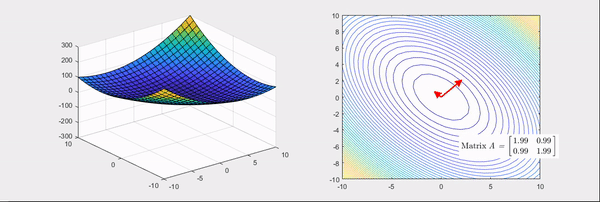
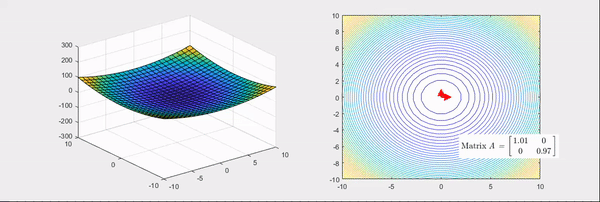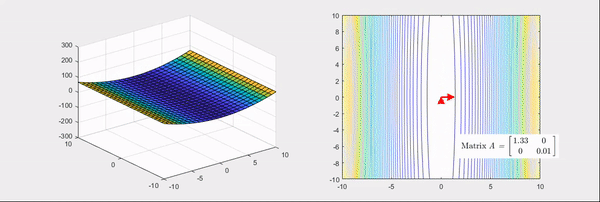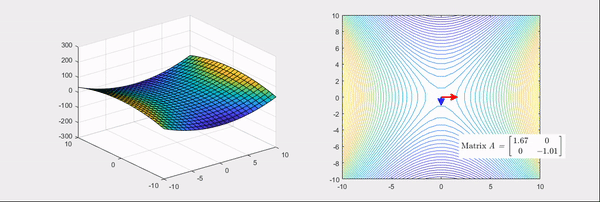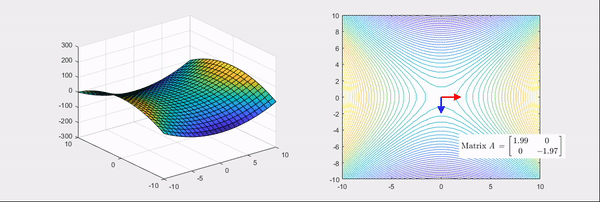
Let’s look at the Hessian’s geometric meaning in detail through examples. The Hessian matrices corresponding to Figure 2 and 3 are as follow;
\[\begin{bmatrix}2 & 1\\1 & 2\\\end{bmatrix} and \begin{bmatrix}2 & 0\\0 & -2\\\end{bmatrix}.\]The things to note here are, the eigenvectors of the Hessian matrix represent the principal axis of transformation and the eigenvalues represent the degree of transformation. More specifically, if the eigenvalues are all positive (Figure 2), it makes the given function more convex. Conversely, if the eigenvalues are all negative, it makes the given function more concave. However, if some of the eigenvalues are positive, and some are negative (Figure 3), the given function is converted to a saddle shape. To recapitulate, by using the main feature of the geometric transformation shown by the Hessian, we could emphasize the gradient change of the given function.
Applications
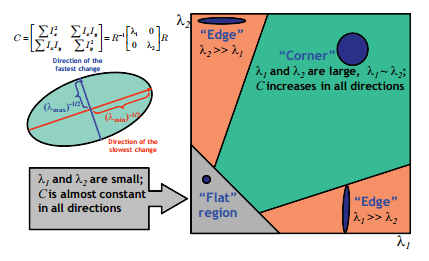
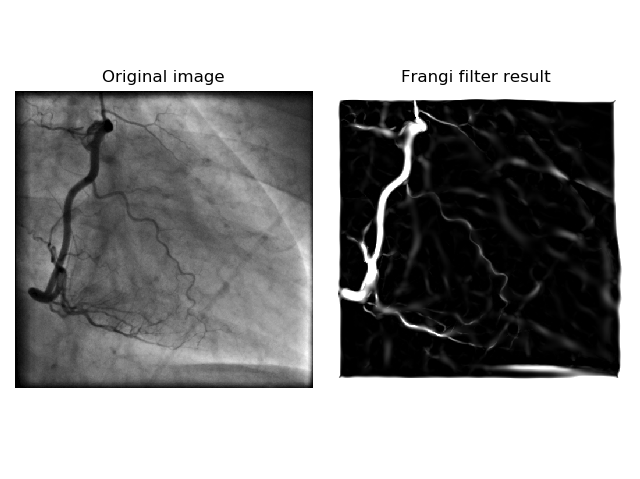
Using the feature that the Hessian emphasizes the gradient change, it can be used as a filter that detects the contour (edge) of a specific object in a given image, which is considered as a function at this point. Figure 4 shows the description of edge detection and the Hessian’s eigenvalues, and Figure 5 shows an application detecting the vessel using the Hessian.
References
[1] “Hessian matrix,” Wikipedia, 24-Jun-2020. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hessian_matrix. [Accessed: 21-Jul-2020].
[2] Y. D. Yeo, “Geometrical meaning of Hessian Matrix,” 17-Jun-2020. [Online]. Available: https://angeloyeo.github.io/2020/06/17/Hessian.html. [Accessed: 21-Jul-2020].
[3] “Hessian Matrix of the image,” Stack Overflow, 01-Sep-1963. [Online]. Available: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/22378360/hessian-matrix-of-the-image. [Accessed: 21-Jul-2020].