The structure of the deep learning model is designed differently depending on the types of data features and the objective of the model. More specifically, in order to select the type of layer used in the model, the characteristics of data features and the learning objectives of the model must be considered.
In order to find out which structure is most suitable, we experimented with fixing the type of dataset and the target of the model and changing the structure of the model. The dataset used in the experiment is MNIST. The types of models used in the experiment were as follows; DenseNet using only dense layer, ConvNet using convolutional layer, and LstmNet using LSTM layer.
Full code of the experiments can be found at the following github repository.
This post was written with reference to the following materials.
- Aymeric Damien’s GitHub > Neural Network Example
- Aymeric Damien’s GitHub > Convolutional Neural Network Example
- Irhum Shafkat’s Medium posting > Intuitively Understanding Convolutions for Deep Learning
- Aymeric Damien’s GitHub > Recurrent Neural Network Example
- Simplilearn > Recurrent Neural Network Tutorial
- Park’s SlideShare > Understanding LSTM
Model Structures
Dense Model
This model consisted only of dense layers. This is the simplest model of the neural network and works well for all types of data, but performance decreases when an input data becomes complicated or large. Therefore, dense layers are used in learning simple data. In addition, in the case of learning complex data, dense layers are used in the last part of the model, which is the stage where features are extracted and get simple enough.
CNN Model
This model consisted of convolutional layers. This model is suitable when there are spatial relationship across the data. Figure 1 depicts how a convolutional layer works, and it helps understand why this model works well when there are spatial relationship across data.
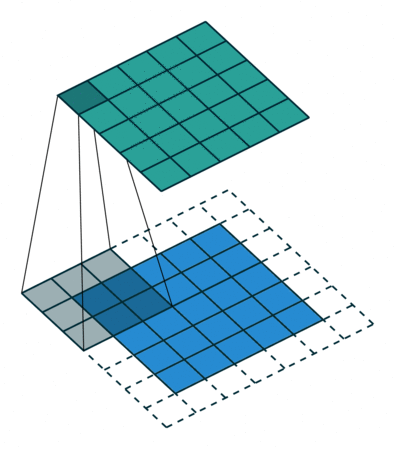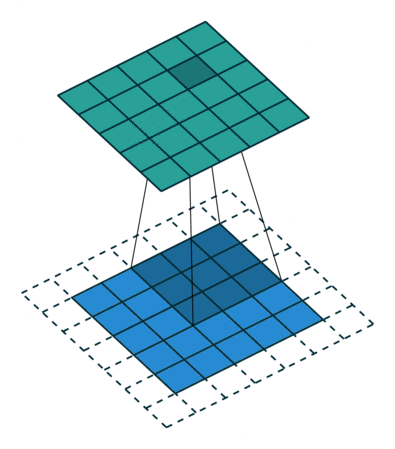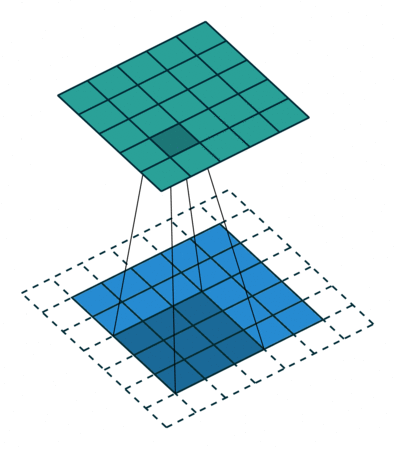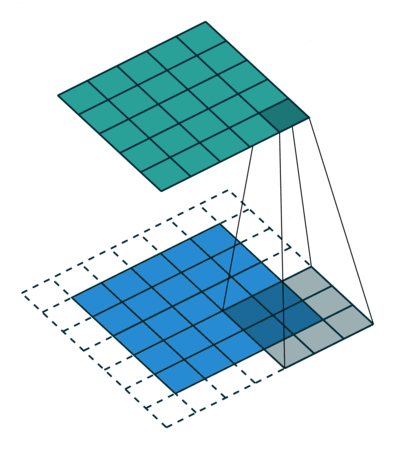
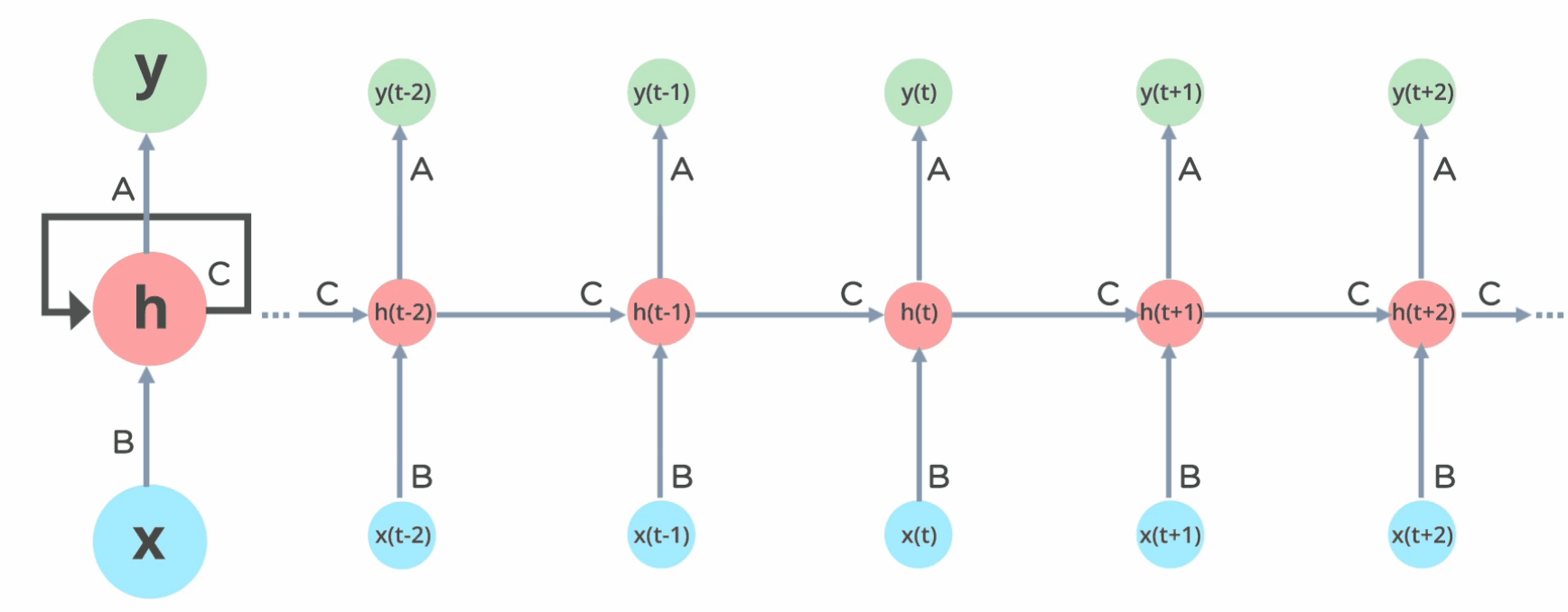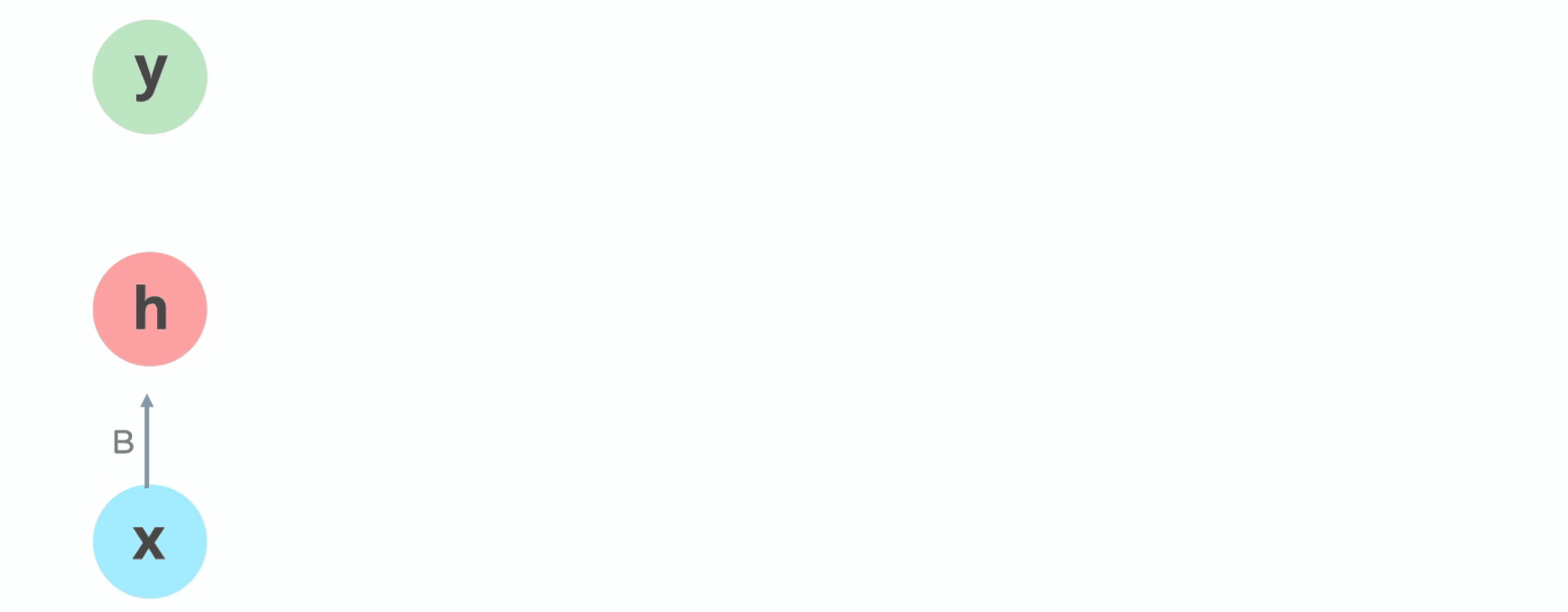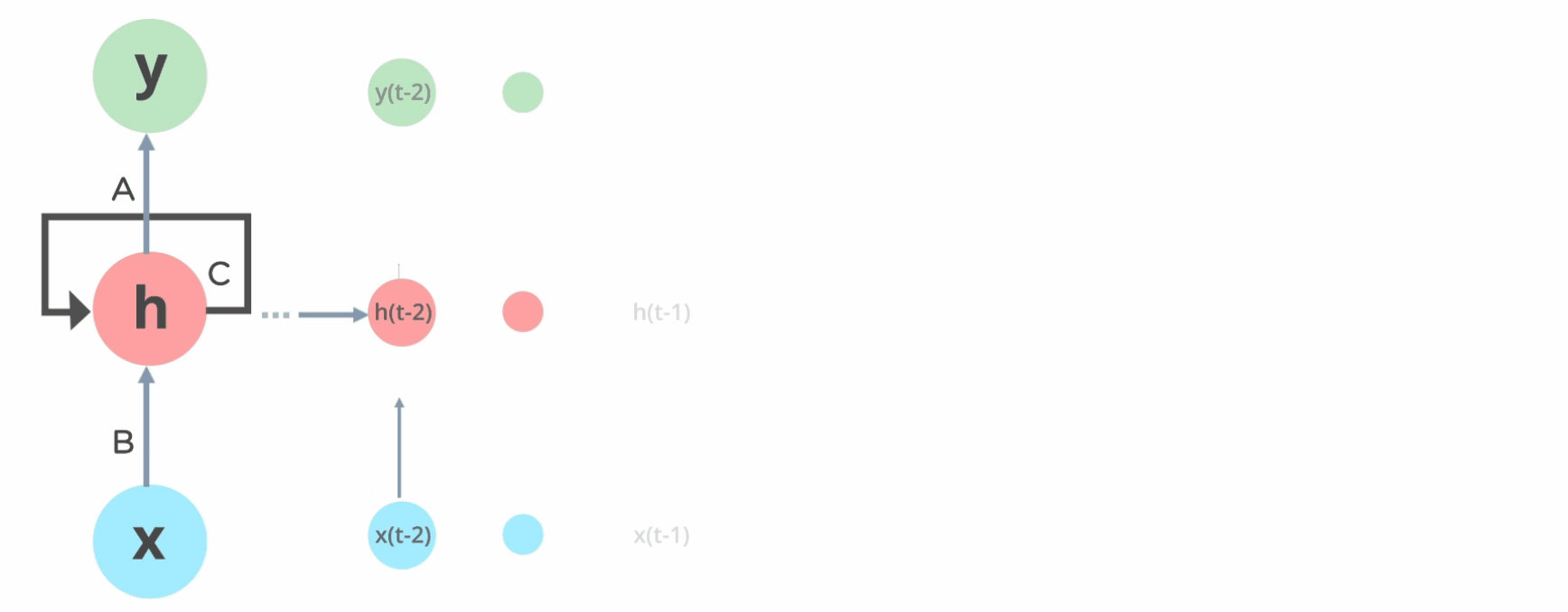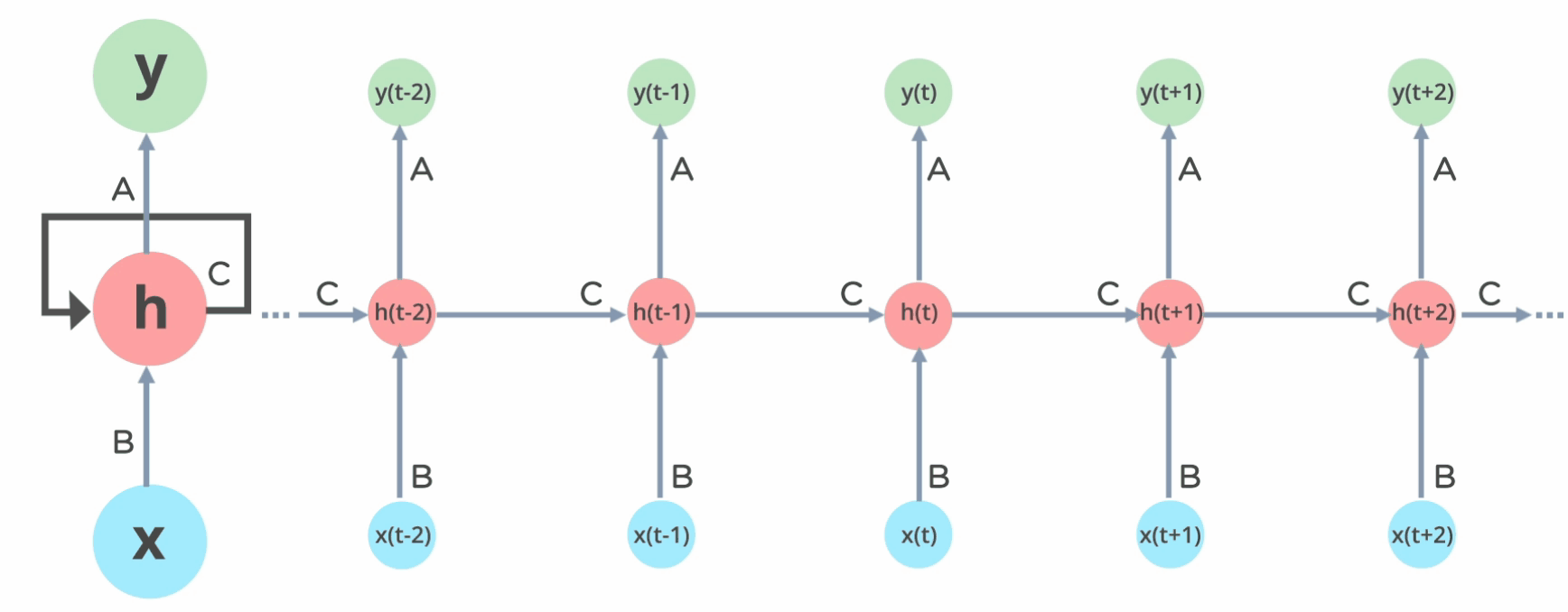
RNN(LSTM) Model
This model consisted of LSTM layers. This model is suitable when there are temporal (sequential) relationship across the data. Figure 2 depicts how a LSTM layer works, and it helps understand why this model works well when there are temporal relationship across data.
Experiment Result
As a result of the experiment, the CNN model using a convolutional layer showed the highest performance for learning MNIST image data. Direct comparison was not possible because the number of trainable parameters differed for each model, but the result was obtained by adjusting hyper-parameters to obtain the best performance for each model.
To sum up, we have confirmed that it is best to use a convolutional layer when learning MNIST image data.
| Accuracy | Loss | |
|---|---|---|
| DenseNet | 0.9556 | 1.5092 |
| ConvNet | 0.9817 | 1.4793 |
| LstmNet | 0.9603 | 1.5015 |
Future Study
In some cases, such as image data or stock data, we can know the nature of the feature data in advance and use the CNN or RNN layers respectively. However, it is difficult to fully understand the charactieristic of completely new feature data. In this case, it is difficult to make assumptions about the temporal/spatial relationships across the data. As a result, it is not easy to decide which layer to use.
Transformer is a model designed to solve this problem. Transformer is a model based on attention, it make no assumptions about the temporal/spatial relationships across the data [3]. In the next posting, we will discuss the structure and application of the Transformer.
Reference
[1]I. Shafkat, “Intuitively Understanding Convolutions for Deep Learning,” Medium, 07-Jun-2018. [Online]. Available: https://towardsdatascience.com/intuitively-understanding-convolutions-for-deep-learning-1f6f42faee1. [Accessed: 23-Jul-2020].
[2] A. Biswal, “Recurrent Neural Network Tutorial,” Simplilearn.com, 28-Apr-2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/deep-learning-tutorial/rnn. [Accessed: 23-Jul-2020].
[3] “Transformer model for language understanding : TensorFlow Core,” TensorFlow. [Online]. Available: https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/text/transformer. [Accessed: 23-Jul-2020].